Causes of osteochondrosis
- genetics;
- Back injuries;
- Congenital or acquired structural defects of the musculoskeletal system (flat feet, postural changes);
- Metabolic failure caused by diseases of endocrine organs;
- Malnutrition and excess weight;
- viral and bacterial infections;
- Lifestyle: Lifting and carrying heavy objects, working in air currents, constant vibration, lack of physical activity;
- persistent psycho-emotional overload;
- Bad Habits: Smoking, alcohol, opioids.
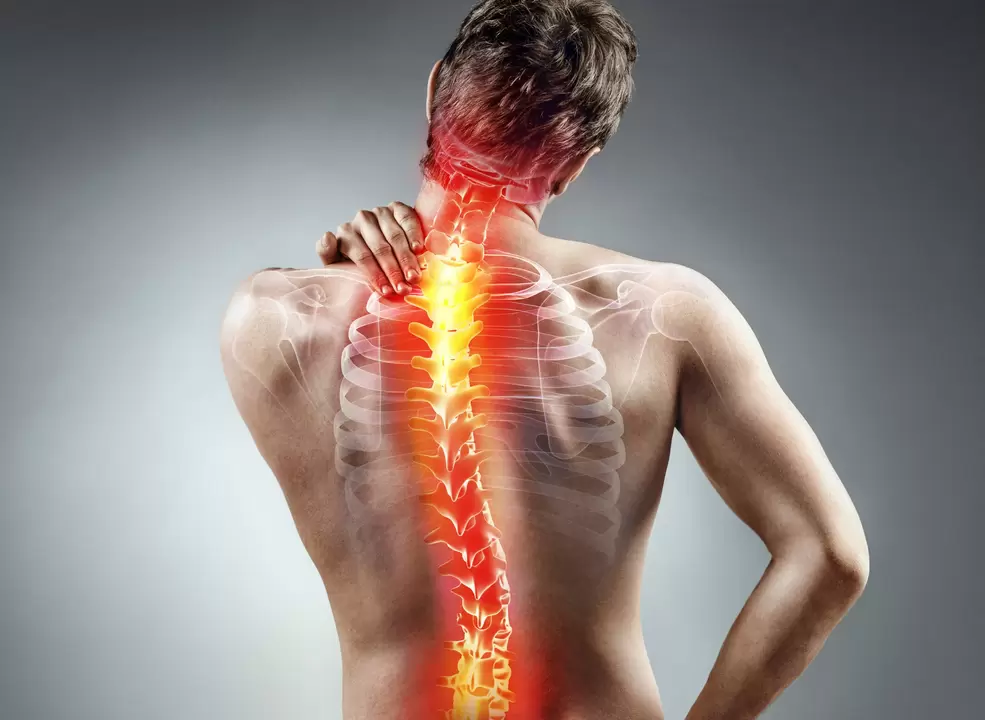
Spinal Osteochondrosis: Types
Lumbar osteochondrosis.
cervical osteochondrosis
Thoracic osteochondrosis
General process
Stages of Osteochondrosis and Possible Complications
- The discs become less elastic. The disc may be slightly deformed; the inner nucleus pulposus is displaced within the disc. This stage either doesn't show up at all or there is mild pain.
- In the second stage, the disc may crack and the surrounding ligaments weaken. The connections between the vertebrae become unstable. Acute pain occurs and results in impairment of work ability.
- The third stage is characterized by complete disc damage. A herniated disc occurs when the nucleus pulposus extends beyond the disc. Spinal deformation or nerve root compression may occur.
- In the fourth stage, surrounding tissues are affected - vertebrae, ligaments, spinal cord membranes. As a result, spinal segments may completely lose mobility.
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis
- Vascular ultrasound can reveal the extent of circulatory disorders, such as the vertebral arteries;
- X-ray of the spine;
- CT also uses X-ray methods, but allows you to build a three-dimensional image of the area under study and detect minute displacements of the vertebrae;
- MRI specializes in soft tissue and allows you to evaluate the condition of your spinal cord and visualize the internal structures of your spinal discs.
- The first and very important remedy for osteochondrosis is lifestyle. Normalization of working conditions, moderate and regular exercise, and healthy sleep significantly improved the patient's condition.
- For medical treatment of osteochondrosis of the spine, a neurologist or general practitioner may prescribe medication. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are most commonly prescribed - this is the standard treatment for osteochondrosis of the spine. They can relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Muscle relaxants help reduce muscle spasms. Vitamins and antioxidants protect nerve tissue from damage. However, any medication has side effects, such as NSAIDs, which can have a negative impact on the stomach.
- In addition to medication, physical therapy such as massage for osteochondrosis of the spine and manual therapy may be used. If severe complications of osteochondrosis develop, surgery may be necessary, but only if long-term conservative treatment has failed.